Latent Heat
Latent Heat: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Latent Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporisation, Latent Heat of Sublimation, Temperature Versus Heat Graph for Heating of Ice, and Heat Capacity of Solids.
Important Questions on Latent Heat
The amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of solid into gas is
Heat is supplied to a solid to raise its temperature across its melting point and boiling point Which of the following graphs correctly represents the relation between heat supplied and temperature ?
The quantity of heat required to convert the unit mass of a substance from its liquid state to the gas state, at its boiling point without any change in its temperature is called the latent heat of fusion.
Observe the following temperature Vs. time graph and fill in the blank:
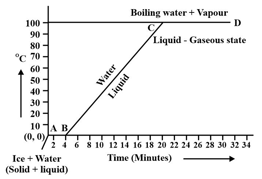
During transition of solid phase to liquid, the object absorbs _____ energy, but its temperature does not increase.
A block of ice at is slowly heated and converted to steam at . Which of the following curves represent the phenomenon qualitatively?
Latent heat depends on the mass of the substance.
The value of latent heat of fusion of ice is .
Define latent heat of a substance and its SI unit?
A container has 4.2 litres of water at . Heat required to boil water in is
Define heat capacity and write its unit.
Observe the following temperature Vs. time graph and fill in the blank:
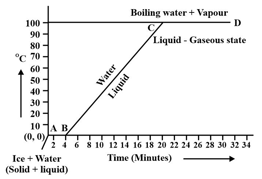
During transition of solid phase to liquid, the object absorbs _____ (electric \chemical \heat) energy, but its temperature does not increase.
Observe the following temperature Versus time graph and fill in the blank.
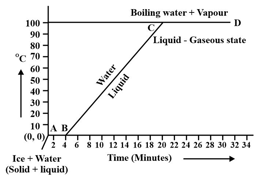
The constant temperature, at which the ice converts into water is called the _____ point of ice.
(Choose from: boiling/melting)
Observe the following temperature Versus time graph and fill in the blank.
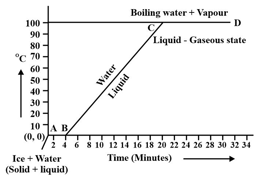
When ice is heated it melts at _____ and converts into water at this constant temperature.
(Choose from: /)
A copper wire long is stretched by . If the energy stored in the stretched wire is converted to heat, calculate the rise in temperature of the wire. (Given: , Density of copper and Specific heat of copper
The specific latent heat of vaporisation for water is large.
The correct reason behind cooling of a room after the water has been sprinkled is
When sun rays are focused on an ice block using a lens of diameter , of ice got melted in . Calculate the heat received per minute per square centimetre. (Latent heat of ice )
What is the unit of latent heat? (Choose from newton, joule, celsius)
A closed bottle containing water at is open on the surface of the moon. Then-
At , a lead bullet of 50g, is fired vertically upwards with a speed of 840 m/s. The specific heat of lead is 0.02 cal/ . On returning to the starting level, it strikes to a cake of ice at . Calculate the amount of ice melted (Assume all the energy is spent in melting only)
